Is PPI and DPI the Same
What is the difference between DPI and PPI, and why does it matter when adjusting and resizing images for print?
Many photographers and designers struggle with these terms, yet understanding them can transform a blurry, poorly sized picture into a crisp, professional-looking work.
In this article, we’ll demystify these concepts and explain what really counts when resizing, so your footage always turn out perfectly.
What is DPI?
DPI indicates resolution of your photos, showing how many individual ink dots a press places per linear inch on a physical surface.
Unlike screen pixels, DPI refers to the actual distribution of paint, affecting the clarity, specification, and color accuracy.
Key Points:
- Quality: Higher DPI results in smoother gradients, sharper lines, and more precise tone transitions.
- Industry standards: Printing typically spreads from 300 to 1200 DPI, depending on the material and desired outcome.
- Device-dependent: DPI is determined by the machine, not the file.
- Digital-to-physical translation: Converts desktop information into tangible attribute, translating pixels into accurate ink patterns.
Ranges of DPI
| Volume | Applications | Nuances |
|---|---|---|
| 72–150 | Drafts, web previews, newspapers | May look pixelated at larger sizes; suitable for rough layouts or text. |
| 200–300 | Books, brochures, general photos | Offers clear result while keeping sizes manageable; standard fidelity. |
| 600–1200 | Professional photographs, fine art, detailed graphics | Captures subtle tones and intricate sequences; used for high-quality output. |
| Above 1200 | Labels, microprinting, specialty reproductions | Exceeds normal visual limits at typical viewing distance; precise work. |
How to check DPI?
1. Looking DPI for Encoded Files
Images store pixel dimensions, not inherent DPI, until mapped to a hardcopy format. To inspect or adjust sharpness:
Windows:
- Right-click the footage > "Properties" > "Details".
- Search for "Horizontal" and "Vertical Resolution".
Mac:
- Open the picture in "Preview" > "Tools" > "Show Inspector" > "General/Info".
- The PPI value serves as the plotter density reference.
Reproduction size formula:

2. Estimating DPI for Physical Prints
- Visual examination: High-resolution media content has fine, densely packed dots; lower-quality ones show distinct patterns.
- Scanning method: Copy at a known PPI (e.g., 1200), then divide pixel measurements by the measured substantial size to calculate DPI:

- Documentation: Manufacturer specs or driver settings indicate maximum granularity for different modes.
3. Professional Measurement Instruments
- Magnifiers or digital microscopes: Allow precise evaluation of dot fraction.
- RIP software: Calculates effective DPI and monitors dot gain in commercial workflows.
How to increase DPI of image?
A. Non-Resampling Change DPI Option
Tools: Adobe Photoshop, Affinity Photo, GIMP
Process:
- Open the file > "Image" > "Size" (or equivalent).
- Disable "Resample" to retain original data.
- Raise DPI; dimensions decrease proportionally, keeping image sharpness intact.
B. Pixel Interpolation / Upscaling
Tools: Same as above, plus AI-based upscalers (Topaz Gigapixel, Adobe Super Resolution).
Process:
- Enable "Resample".
- Choose an algorithm:
- Bicubic Smoother / Lanczos for enlargements.
- Bicubic Sharper for minor increases.
- Set target DPI and proportions.
Note: Interpolation estimates additional pixels between existing ones. Overuse can create artifacts or blur fine edges.
C. Advanced Image DPI Reproduction Practices
- RIP Software: Optimizes effective DPI, manages dot gain, and ensures precise rasterization.
- Screening methods (FM/AM): Influence perceived detail; higher DPI may not improve results if the halftone process is limiting.
What is PPI?
PPI measures the concentration of pixels in a digital image or display, indicating how many units fit within a single linear inch. It is a standard that steers scaling and quality without adding extra information to the file.
Key Points:
- Sharpness: Higher PPI leads to clearer, more defined pictures on monitors.
- Printing: Determines how pixels are translated into stamped dots, affecting final size and precision.
- Metadata vs Content: Modifying PPI without resampling changes lithograph dimensions while retaining all original elements.
- Professional Utilization: Essential for prepress, publishing, and high-resolution workflows.
Ranges of PPI for Printing
| Volume | Use | Perceived Clarity |
|---|---|---|
| 72–96 PPI | Legacy, basic monitors | Adequate for simple viewing; limited attributes |
| 100–150 PPI | Low-resolution images, slides | Noticeably clearer; tailored for casual purposes |
| 150–220 PPI | Tablets, mid-tier screens | Defined visuals; good for reading and plain artwork |
| 220–300 PPI | Modern smartphones, high-res desktops | Crisp rendering; ideal for intricate graphics |
| 300–500 PPI | Retina and professional setups | Extremely detailed; suitable for editing and design |
| 500+ PPI | Micro-displays, VR devices | Ultra-precise; fine elements fully visible |
How to check PPI of image?
1. Calculating PPI
Pixel thickness can be determined using the pixel count relative to its intended measurement:

- Dimension: total horizontal or vertical pixels
- Physical Size: target press or panel length along the same axis
Example:
- Pixel width = 3600 px
- Publication width = 12 in
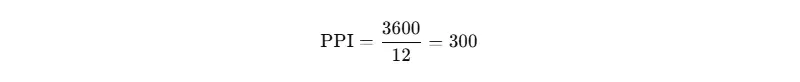
2. Applications
- Adobe Photoshop:
- Go to "Image" > "Size"
- Check "Resolution"; undo "Resample" to customize size without changing bit map
- GIMP:
- Navigate to "Image" > "Print Size"
- X and Y indicate density; modify proportions without affecting pixel data
3. Automated / Code-Based

How to increase PPI of image?
When you change PPI of image without altering pixel count, it reduces physical dimensions. Increasing with resampling adds more dots, allowing larger graphics at higher clarity.
Way 1. Editing Software
Adobe Photoshop
- Open the picture.
- Enable "Resample" to create additional pixels: choose "Preserve Details 2.0" for minimal quality loss.
- Enter desired PPI, click "OK"
GIMP
- Launch footage "Image" > "Print Size".
- Adjust X/Y resolution.
- To increase matrix size, scale via "Image" > "Scale" using interpolation.
Way 2. Automated Approach*
Python (Pillow)

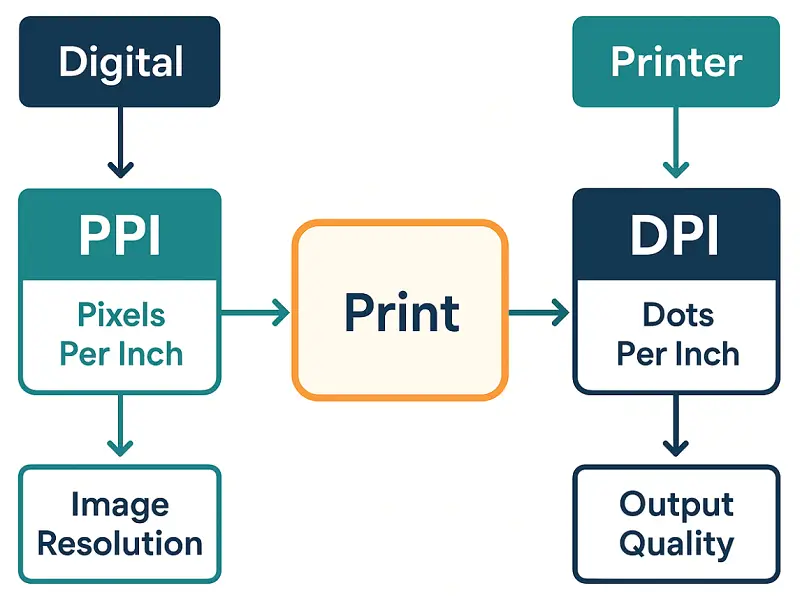
DPI vs PPI
Grasping the DPI and PPI difference is essential for specialists handling media. The table below provides a technical comparison highlighting operational, perceptual, and computational aspects:
| Feature | DPI (Dots Per Inch) | PPI (Pixels Per Inch) |
|---|---|---|
| Basis | Physical deposition of paint on paper | Number of pixel elements per linear inch |
| Control Mechanism | Printer driver configuration, nozzle precision, halftoning strategies | Editing parameters, resampling algorithms, export settings |
| Effect on Detail | Influences micro-level texture | Determines fine structures and zooming |
| Device Dependency | Printer model (inkjet, laser, offset), substrate absorption | Display resolution, monitor dimensions |
| Scaling Considerations | Increasing DPI improves printed smoothness without altering data | Raising PPI without resampling reduces size |
| Technical Constraints | Nozzle density, viscosity, texture | Native grid, interpolation limits |
| Evaluation Metrics | Line screen, dot gain, color gamut fidelity | Pixel thickness per inch, effective resolution for output |
| Workflow Implications | Prepress adjustments, printer calibration, RIP software | Image retouching, resampling strategy, export format selection |
Is PPI and DPI the Same - Conclusion
In summary, understanding DPI vs PPI is important for producing high-quality visuals across digital and physical formats.
Grasping their interaction enables photographers, designers, and print specialists to change image size without compromising sharpness, clarity, or proportions.
With careful consideration of these factors, illustrations can maintain precision on screens, retain aspect in printed materials, and consistently meet professional standards.