What is a Good Bitrate for Recording
Determining the good bitrate for recording digital media is crucial for balancing file size, quality, and delivery requirements. Whether it's audio or video content, selecting the right bitrate can significantly impact the viewing or listening experience.

In this article, we'll explore:
- What is bitrate?
- What factors influence bitrate selection?
- What is a good bitrate for recording different video and audio content?
At the end, you will have recommendations for choosing the best audio and video bitrate for your digital media projects.
What is bitrate's definition?
Bitrate refers to the amount of data processed per unit of time in digital communication or multimedia. It's commonly used to describe the quality of audio or video data streams. In simpler terms, bitrate measures how much information is conveyed in a given amount of time.
Bitrate is usually expressed in kilobits per second (Kbps) or megabits per second (Mbps). Higher bitrate in an audio or video typically means better quality and fewer compression artifacts. However, it also requires more storage space and higher bandwidth for streaming.
There are two bitrate types:
- Constant Bitrate (CBR). The bitrate remains constant throughout the entire duration of the multimedia file. CBR is often used in applications where maintaining a consistent file size is important, such as live streaming or broadcasting.
- Variable Bitrate (VBR). This bitrate allows for more efficient use of data by allocating higher bitrates to complex segments of the media and lower ones to less demanding parts. This results in better overall quality and compression efficiency compared to CBR. VBR is commonly used in applications where preserving quality while optimizing file size is a priority. These include video-on-demand services or music streaming.
Why does bitrate matter for screen recording?
Just as for producing multimedia, bitrate is crucial for screen recording because it directly impacts the quality and clarity of the content.
When you're capturing what's happening on your screen, whether it's for creating video guides, demonstrations, or gameplay videos, you want to ensure that the recording accurately represents what you're showing.
Why video bitrate is important for screen recording:
- Quality of Capture. A higher bitrate means more data is being recorded per second. This translates to better-quality video with sharper images, smoother motion, and fewer compression artifacts. This is especially important for capturing detailed visuals, such as text, graphics, or fine details in software interfaces.
- Readability of Text. Many screen recordings involve displaying text, such as in tutorials or presentations. Higher bitrate recordings preserve the clarity and legibility of text. Hence, it ensures that viewers can easily read what's on the screen without it appearing blurry or pixelated.
- Smoothness of Motion. Screen recordings often involve capturing dynamic content, such as moving cursors, animations, or video playback. A higher bitrate helps maintain smooth motion and reduces the likelihood of blur or stuttering, resulting in a more polished and professional-looking recording.
- Retention of Details. Whether it's capturing intricate design elements, subtle color gradients, or small icons, a higher bitrate ensures that the recording retains as much detail as possible. This allows viewers to see the content exactly as it appears on your screen.
- Size Management. Balancing it is crucial because while higher bitrates improve visual fidelity, they also increase file size, which can affect storage capacity and upload times.
Overall, choosing the right bitrate for screen recording is essential to producing high-quality videos that effectively convey the information you're trying to share.
Common bitrates and their applications
Bitrates vary depending on the type of media being encoded, whether it's audio or video. Here are some typical bitrates and their use.
Audio Bitrates: Comparison table
| Bitrate | Application | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 64 kbps | Often employed for voice calls and podcasts where bandwidth is limited. | While it reduces file size significantly, sound clarity may suffer. |
| 128 kbps | This bitrate is commonly used for streaming music online, including platforms like Spotify and Apple Music. | While it offers decent audio quality, some compression artifacts may be noticeable, particularly in complex or dynamic music. |
| 192 kbps - 256 kbps | These bitrates provide better audio quality compared to 128 kbps and are often used for higher-quality music streaming or downloading. | They strike a balance between audio quality and file size, suitable for listeners who prioritize fidelity but also consider storage or bandwidth constraints. |
| 320 kbps | Considered near-CD quality. This bitrate offers excellent audio accuracy and is often preferred by audiophiles or individuals who aim for the highest possible sound quality. | It's commonly used for music downloads or premium streaming services that offer high-fidelity audio options. |
Video Bitrates: Comparison table
| Bitrate | Application | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1-2 Mbps | This bitrate range is suitable for streaming standard-definition (SD) video content, such as online clips or video calls. | It provides acceptable quality for smaller screens or lower-resolution displays. However, it may exhibit compression artifacts or reduced detail on larger displays. |
| 3-6 Mbps | Ideal for streaming high-definition (HD) video content, including platforms like YouTube or Netflix. | This bitrate range offers sharper image quality, smoother motion, and fewer compression artifacts, suitable for most viewing environments and screen sizes. |
| 10-20 Mbps | Used for streaming or downloading full high-definition (Full HD) video content, offering even higher quality and clarity compared to lower bitrate streams. | This bitrate range is suitable for larger screens or higher-resolution displays, providing immersive viewing experiences with enhanced detail and fidelity. |
| 25 Mbps and above | Reserved for ultra-high-definition (UHD) or 4K video content, offering the highest level of detail and visual fidelity. | This bitrate range ensures optimal quality for viewing on large screens or high-resolution displays, delivering stunning visuals with minimal compression artifacts. |
These are general descriptions, and specific bitrate requirements may vary depending on factors such as the content's complexity, intended audience, available bandwidth, and playback device capabilities.
How does bitrate affect the file size?
While aiming for the best quality, it's also important to strike a balance between bitrate and file size. Remember, bitrate directly influences the size of video and audio files. Essentially, the bitrate determines how much data is used to represent each unit of time in the media stream.
Higher bitrates allocate more data to encode each second of the media. This results in more detailed and higher-quality representations of the audio or video content. Conversely, lower bitrates use less data per second.
Bitrate calculation
To estimate the size of a media file based on its bitrate, you can use the following formula:
File Size (in bytes) = Bitrate (in bits per second) × Duration (in seconds) / 8
For example, you have a video with a bitrate of 5 Mbps (5,000,000 bits per second) and a duration of 10 minutes (600 seconds). Then, the estimated file size would be: (5,000,000 bits/s) × (600 s) / 8 = 375,000,000 bytes (or 375 MB).
In summary, finding the right balance between bitrate, file size, and desired quality is essential when encoding media for storage, streaming, or distribution.
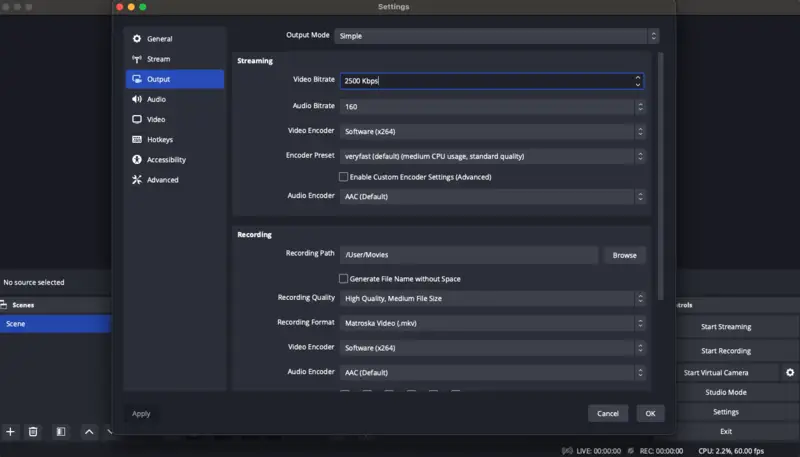 Choosing audio and video bitrate for streaming with OBS Studio.
Choosing audio and video bitrate for streaming with OBS Studio.
Recommended bitrates for different purposes
When working on various platforms, you may get confused with what bitrate to use where. Save the table below to never get lost anymore.
For screen recording, a bitrate of around 4-8 Mbps should be sufficient for Windows computers to ensure good quality and detail capture.
| Type of video | Resolution | Recommended Video Bitrate |
| Best YouTube Video Bitrate | 1080p (Full HD) | 8-12 Mbps |
| 720p (HD) | 5-7 Mbps | |
| 480p (Standard Definition) | 2-4 Mbps | |
| Best Bitrate for YouTube Streaming | 1080p (Full HD) | 4-6 Mbps for video, 128-192 kbps for audio |
| 720p (HD) | 2.5-4 Mbps for video, 128-192 kbps for audio | |
| Best Video Bitrate for YouTube Shorts | various resolutions | A bitrate of 2-4 Mbps is good for most cases |
| Best Bitrate for Instagram Reels | various resolutions | A bitrate of around 2-4 Mbps should be suitable |
| Best Instagram Story Bitrate | various resolutions | A bitrate of 2-4 Mbps is recommended |
| Best TikTok Video Bitrate | various resolutions | A bitrate of around 2-4 Mbps should provide good quality for most videos |
| Best Facebook Video Bitrate | 1080p (Full HD) | 4-6 Mbps |
| 720p (HD) | 2.5-4 Mbps | |
| 480p (Standard Definition) | 1-2 Mbps | |
| Best Video Bitrate for Twitch Streaming | 720p to 1080p | 4,500 to 6,000 Kbps for video, 160 kbps for audio |
What is a good bitrate for screen recording: FAQ
- What is the ideal bitrate for recording audio?
- For professional use, such as podcasting or music production, 320 kbps is often considered the sweet spot for MP3 audio. If recording in uncompressed formats like WAV or PCM, the bitrate is more about sample rate and bit depth, not a direct value.
- Does a higher bitrate always result in better quality?
- Not always. While higher bitrates can improve quality, diminishing returns apply. For example, beyond a certain point, the human eye or ear may not discern much of a difference. The codec used for compression also plays a significant role. Modern codecs like H.264 and H.265 are more efficient, meaning you can achieve high-quality recordings at lower bitrates compared to older formats.
- How can I test the bitrate of my recordings?
- Most audio or video editing software allows you to check the bitrate of a file. In audio, you can use a tool like Audacity to inspect MP3 bitrates. Video files can be analyzed with software like HandBrake or MediaInfo.
- What is the difference between bit depth and bitrate?
- Bit depth refers to the amount of data used to represent each sample in an audio recording, affecting the dynamic range and the overall quality. Bitrate determines the quality and file size of compressed audio.
- What is the best bitrate for podcasting or voiceovers?
- 128 kbps to 192 kbps is generally sufficient. For HD screen recording, especially for music or professional-grade podcasts, you might go as high as 256 kbps or 320 kbps.
What is a good bitrate for recording: conclusion
Selecting the best bitrate for encoding digital media involves careful consideration of multiple factors, including content characteristics, audience expectations, and delivery constraints.
By understanding the impact of bitrate on file size, quality, and streaming performance, content creators can optimize their settings to deliver an optimal viewing or listening experience.
Whether you're determining the best streaming bitrate or good screen recording bitrate, strike for the right balance between quality and efficiency. In this way, you'll achieve success in digital media production.
Co-authors